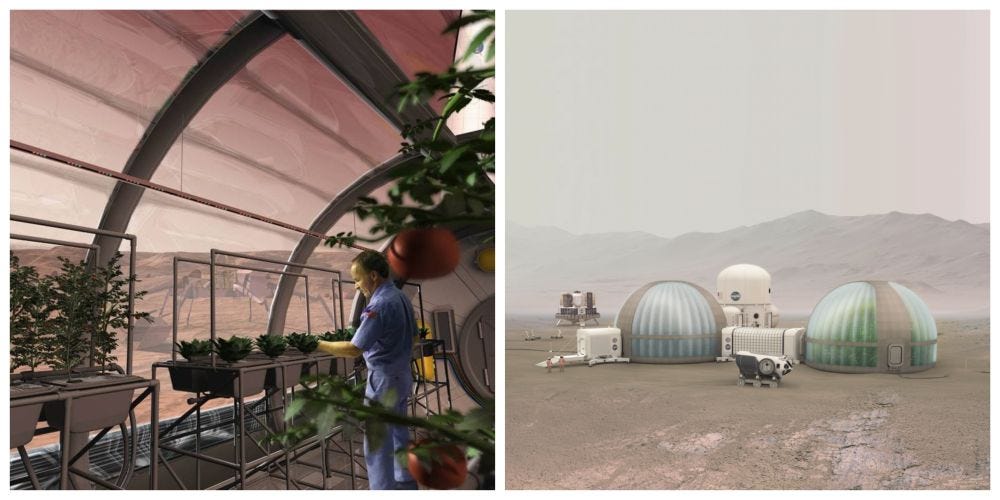
Martian colonies of the future will require vast quantities of food, but bringing an endless stream of foodstuffs from Earth would be costly and dangerous. The best answer to this conundrum is to grow food in greenhouse, specially constructed for that purpose. However, such a system would likely require large quantities of topsoil as a growing medium for the plants (water to supply a hydroponic system would probably be in short supply).
University of Georgia (UGA) researchers developed a series of artificial soil mixtures mimicking the topsoil of Mars. These substitute samples of Martian regolith were composed of mixtures of soil, clay, salts, and other components readily available on the surface of Mars.
Investigators examined these the samples, exploring how fertile the ruddy surface of Mars might be.
“Simulating the mineral makeup or salt content of these Martian mixtures can tell us a lot about the potential fertility of the soil. Things like nutrients, salinity, pH are part of what make a soil fertile and understanding where Mars’ soils are at in that spectrum is key to knowing if they are viable and if not, are there feasible solutions that can be used to make them viable,” explained Laura Fackrell, UGA geology doctoral candidate and lead author on the study.
Red acres is the place to be…
Plans are underway at NASA to place the first humans on Mars sometime in the mid 2030’s, but this crew would return to Earth as soon as possible. This group of explorers would be able to bring all the food needed with them for the journey.
The most ambitious plan to colonize Mars comes from Elon Musk and SpaceX, who plan to launch 100,000 colonists to Mars every 26 months. By 2050, the team plans to have one million people on the face of the Red Planet. Large-scale farming on Mars would require the development of significant Martian agricultural infrastructure and production methods.
Despite its thin atmosphere and frigid temperatures, the upper crust of Mars contains many of the nutrients needed by plants, including nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorous.
If you think the ocean isn’t important, imagine Earth without it. Mars comes to mind. No ocean, no life support system. — Sylvia Earle
However, the presence of these chemical components in soil does not mean the growing medium is good for crops. Whether or not these vital components of soil are available to plants remains an additional concern.
“Soil on Mars is known to contain the majority of planet essential nutrients, but many questions of both the benefits (e.g. bioavailability of present nutrients) and limitations (e.g. extent of toxins) of Martian soil as a plant growth medium remain unanswered,” researchers describe in an article published in the journal Icarus, detailing their study.
Simulated Martian soil is dry and crusty, driving researchers to enhance the medium with beneficial bacteria and fungi for farming on Mars, as farmers might do on Earth.
“Specific types of bacteria and fungi are known to be beneficial for plants, and may be able to support them under stress conditions like we see on Mars,” said Fackrell.
With the ability to grow food on Mars, the possibility of colonizing the Red Planet — and beyond — dramatically increases.
In addition to aiding in the future colonization of Mars, this new study could also aid farmers on Earth seeking to grow food in challenging environments.
This article was originally published on The Cosmic Companion by James Maynard, founder and publisher of The Cosmic Companion. He is a New England native turned desert rat in Tucson, where he lives with his lovely wife, Nicole, and Max the Cat. You can read this original piece here.
Astronomy News with The Cosmic Companion is also available as a weekly podcast, carried on all major podcast providers. Tune in every Tuesday for updates on the latest astronomy news, and interviews with astronomers and other researchers working to uncover the nature of the Universe.
Get the TNW newsletter
Get the most important tech news in your inbox each week.