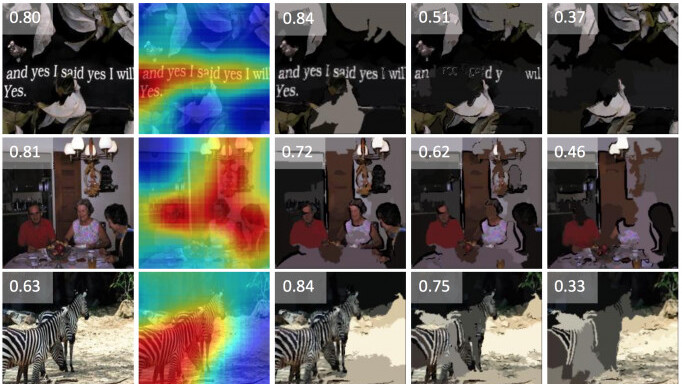
MIT computer scientists have developed a new algorithm that helps determine which parts of your photos are most memorable. The program, called MemNet, uses artificial intelligence to build a heat map which determines the most visually interesting pieces of your photo.
Deep learning algorithms like MemNet use human training in order to “train” the algorithm how to complete complex processes. Over time, the algorithm gets smarter and can perform these tasks as well, or better, than a human.
To train MemNet, researchers gathered tens of thousands of pictures from several datasets. Each picture was then assigned a memorability score based on how well human subjects remembered them after viewing.
Once the training was complete, MemNet went face-to-face against against actual people in an attempt to predict the memorability of a group of images it’d never seen.
MemNet performed 30 percent better than any algorithm of its kind and within a few percentage points of humans.
The program is available online, so I decided to give it a try using a photo I took at the San Diego Zoo last weekend.


MemNet, as you’d expect assigned the brightest reds to the foreground of the image, in areas where there was a lot of flamingo congregation. Other areas were less memorable until you get to the top left of the image, which might as well just get cut off and sent somewhere for use in a nice mosaic or something.
The image scored a memorability rating of 0.598 on a scale of 0 to 1.
Researchers say any image above 0.5 is expected to be remembered by at least 50 percent of people who view it for at least 100 seconds afterward.
Future implications could lead to better image editing applications, more powerful tools for marketers or better educational resources for those who struggle to remember course material.
➤ This New Deep Learning Tool Shows You the Most Memorable Parts of Your Photos [Gizmodo]
Get the TNW newsletter
Get the most important tech news in your inbox each week.




