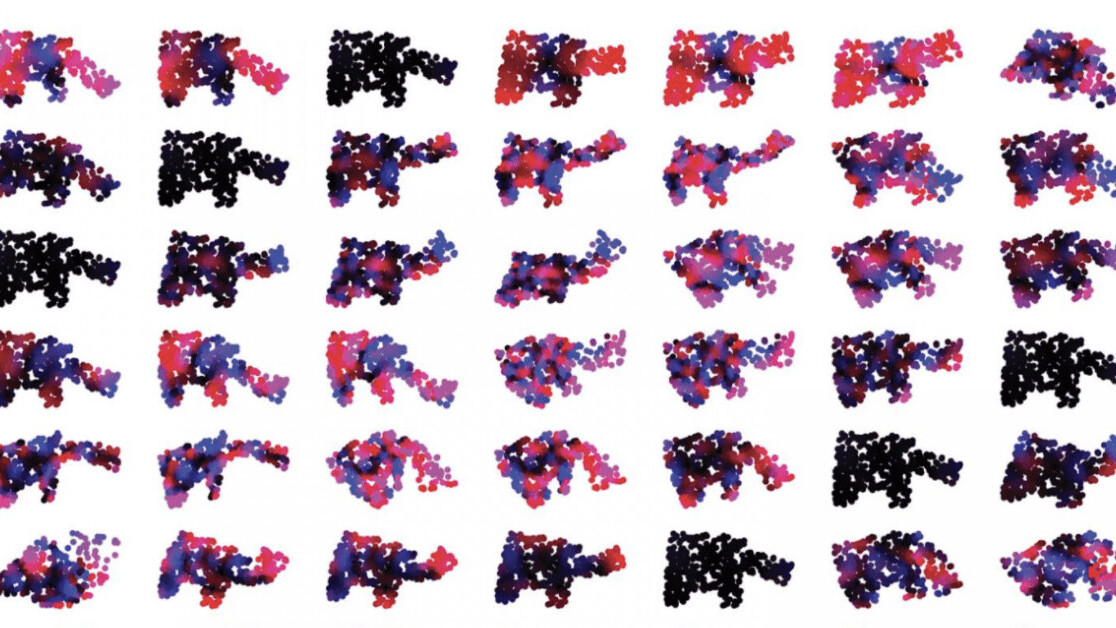
Soft robots can be far more flexible than their rigid relatives, but their vast ranges of motion makes it hard to map the location of their body parts.
A new algorithm could give them greater control of their movements by optimizing the arrangement of sensors on their bodies.
“You can’t put an infinite number of sensors on the robot itself,” said study co-lead author Andrew Spielberg, a PhD student at MIT CSAIL. “So, the question is: how many sensors do you have, and where do you put those sensors in order to get the most bang for your buck?”
The researchers developed a novel neural network architecture to answer the question. It works by determining the ideal location for sensors and learning which motions are needed for different tasks.
[Read: ‘Sensorized’ skin helps robots understand where the hell they are]
The team first divided the robot’s body into different regions, and used their rate of strain as inputs to the neural network. Over time, the network worked out the most efficient sequence of movements to complete tasks, such as which motions to use for gripping different options.
The network also tracks which regions are used most frequently, and then removes the lesser-used areas from the inputs in subsequent trials.
This process enables the system to recommend where to place sensors on the robot.
The researchers tested its suggestions by comparing them to sensor designs made by human experts.
They first asked the roboticists to pick the sensor position they thought would work best for tasks such as grasping items. Next, they ran simulations comparing the performance of the human designs to the algorithm-senzorised robots.
Study co-lead author Alexander Amini said he was surprised by the results:
Our model vastly outperformed humans for each task, even though I looked at some of the robot bodies and felt very confident on where the sensors should go. It turns out there are a lot more subtleties in this problem than we initially expected.
The researchers believe the algorithm could help automate soft robot design and ultimately help machines interact with their surroundings.
Greetings Humanoids! Did you know we have a newsletter all about AI? You can subscribe to it right here.
Get the TNW newsletter
Get the most important tech news in your inbox each week.