A deep learning algorithm developed at MIT has discovered new antibiotics that can treat drug-resistant diseases by killing 35 powerful bacteria.
The pathogens that the halicin antibiotic has targetted include Acinetobacter baumannii, which was nicknamed “Iraqibacter” after it infected thousands of US service personnel returning from the war in Iraq.
In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) named it the bacteria that poses the greatest threat to human health — because of its resistance to antibiotics. The discovery of halicin may be able to change that.
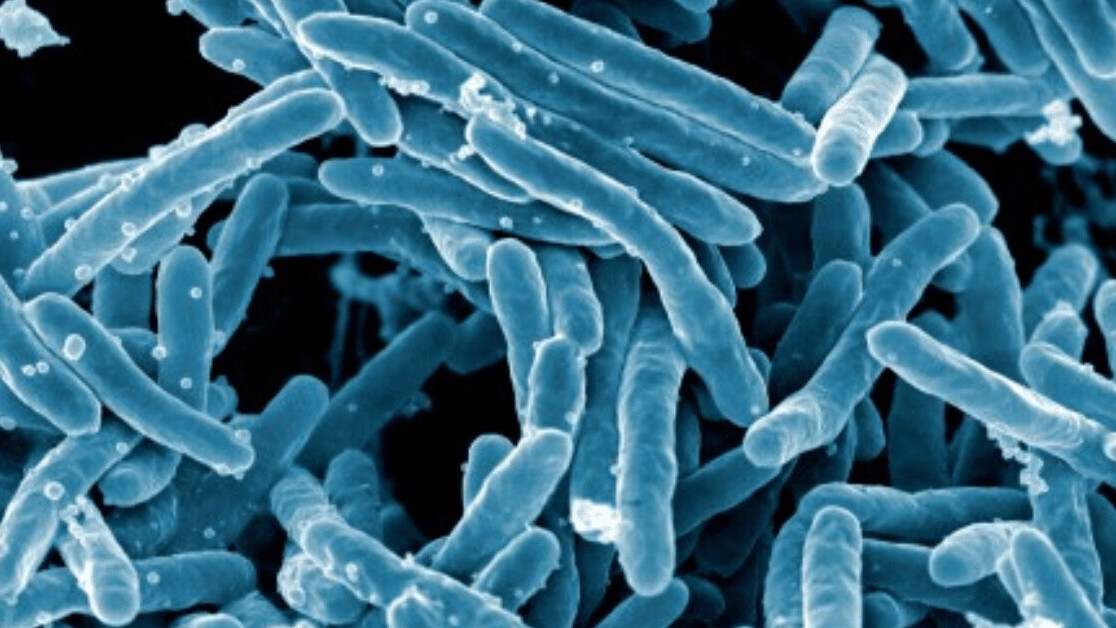
The Financial Times reports that it can also target tuberculosis (pictured above_ and clostridium difficile, a bacteria that can infect the bowel and cause diarrhea.
[Read: Scientists are reengineering viruses to fight antibiotic resistance]
The algorithm that discovered Halicin had been trained to analyze the structure of 2,500 molecules to evaluate their anti-bacterial properties. It then searched a library of 100 million molecules to predict their ability to combat specific pathogens.
From the lab to the market
The algorithm was developed by computer scientist Regina Barzilay, an MIT professor who specializes in applications of deep learning to chemistry and oncology.
“There is still a question of whether machine-learning tools are really doing something intelligent in healthcare, and how we can develop them to be workhorses in the pharmaceuticals industry,” Barzilay said, as per the Financial Times. “This shows how far you can adapt this tool.”
Halicin was one of nine new molecules discovered by Barzilay’s team, who reported their work in a paper published in scientific journal Cell.
There will be significant challenges in bringing their discovery to market, but their work has highlighted drug discovery as one of the most promising applications of AI.
You’re here because you want to learn more about artificial intelligence. So do we. So this summer, we’re bringing Neural to TNW Conference 2020, where we will host a vibrant program dedicated exclusively to AI. With keynotes by experts from companies like Spotify and RSA, our Neural track will take a deep dive into new innovations, ethical problems, and how AI can transform businesses. Get your early bird ticket and check out the full Neural track.
Get the TNW newsletter
Get the most important tech news in your inbox each week.