This week, the US patent office issued 6,746 patents. Each patent adds a little something new to the human knowledge base. As we cannot list all five thousand, the PatentYogi team has selected the six most interesting patents.
Phantom limb gestures can now control computers

A company called Rovi Guides has patented an invention that detects the motions of a non-existing limb and uses it to control operation of a computer.
People with missing limbs generally feel like they still have the limb and can even control its movements. This phenomenon is popularly called phantom limb.
The invention exploits the fact that muscle control of limbs originates in the brain. When a limb is completely missing, there is no way to detect muscle activity. But by sensing activity in certain regions of brain, the movements of the phantom limb may be detected. These movements may then be recognized and used to perform certain operations like controlling a media player.
Detection of phantom limb movement is also possible in cases where an amputee is using an EMG based prosthetic device. When the amputee performs a movement with the phantom limb even with the missing prosthetic device, a unique EMG signature is generated. By sensing and recognizing this EMG signature operations of a computer can be controlled.
Battery-free phones could become a reality

The invention uses piezoelectric micro energy harvester that can convert tiny vibrations in the surrounding into electrical energy. Such vibrations may be a result of natural causes like wind or human activity such as vehicular movement, operation of machines etc.
Since the energy in these vibrations is tiny, it’s important to have high energy conversion efficiency.
So the micro energy harvester is finely tuned to the frequencies of the vibrations.
Since different environments would have different spectrums of vibration frequencies, the invention uses an array of micro energy harvesters each tuned to a separate band of frequencies. This allows the micro energy harvesters to function and provide energy independent of the environment.
By connecting together, a sufficiently large collection of such micro energy harvesters, devices like smart phones and tablets can be powered without needing a battery.
Nano-diamonds used to destroy cancer cells

Quantum dots are nanostructures which can be tailored to absorb and emit light radiation of desired wavelengths. The idea is to get a quantum dot attached to a cancerous cell and then cause it to generate destructive UV rays.
In order to carry the quantum dot to the cancerous cell, the invention uses a target moiety that can specifically bind with cancerous or pathogenic cells.
The target moiety is attached to the quantum dot with a linker and then coated with a biocompatible material such as fat, carbohydrate, protein etc. Boeing calls the resulting compound a “bioconjugated nanoparticle” which is then injected into the blood stream. Once the bioconjugated nanoparticle attaches with a cancerous cell, the patient is exposed to soft x-rays.
The quantum dot is designed to absorb the x-rays and emit UV radiation. This UV radiation then destroys the cell by disrupting its membrane and damaging DNA.
Existing methods of UV radiation therapy can’t reach deep regions of tissue because of limited penetration of UV. And this technique from Boeing can target and destroy cancerous cells throughout the body since x-rays have higher penetrative power.
Self-correcting 3D printer invented by MIT

This 3D printer also has the additional feature of correcting itself in the event of any printing errors.
While the object is being printed, a camera continuously monitors the object. Using machine vision, any deviation from the object’s model is detected and the print is identified as failed.
The 3D printer then proceeds to automatically remove the printed part and discard it before restarting the printing process.
In order to automatically remove and discard the printed part, a motorized blade is used. A solenoid-controlled pneumatic piston moves the blade across the printing surface separating the printed part from the printing surface. The printed part is then disposed.
The technique may also use other mechanisms of removal such as by vibrating the printing surface or using pins that rise from the printing surface from below and push the printed part away.
The same mechanism may also be used to separate the final printed object thus avoiding need for any human intervention.
Method for providing route guidance based on emotion

Existing route guidance systems calculate a route by taking into account only the current position and destination of a vehicle.
The patented method also obtains information about user’s emotional state, and then provides route guidance tailored to a user’s emotional state. Further, it provides audio, video, and lighting corresponding to the user’s emotional state that helps to improve the user’s emotional state.
The invention should help improving the quality of life of regular travellers
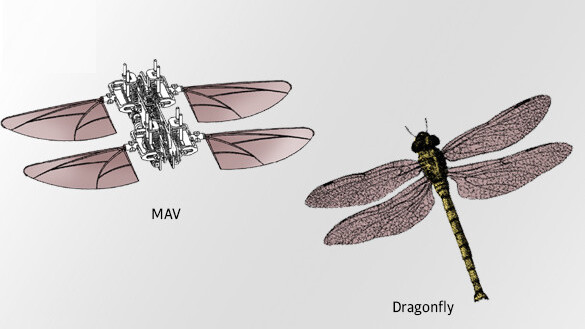
A Micro Air Vehicle (MAV) inspired from a dragonfly

The wings of patented MAV can be transitioned between flapping flight and fixed wing flight to enable gliding and hovering in a single configuration.
The MAV can have independent wing control to provide enhance energy efficiency and high manoeuvrability. Power to each wing can be controlled separately by varying the amplitude of the wing flapping, the frequency of the wing flapping, or both. The flapping frequency can be controlled such that it is at or near the natural frequency of the wings for improved energy efficiency.
MAVs are useful in several applications because their small size and manoeuvrability yields several advantages. For example, MAVs can fly in enclosed or partially enclosed areas, such as in buildings and alleyways. MAVs can also fly through and around obstacles that are too large or too close together to be avoided by conventional aerial vehicles. MAVs can perform tasks that other, larger aerial vehicles cannot.
Get the TNW newsletter
Get the most important tech news in your inbox each week.





